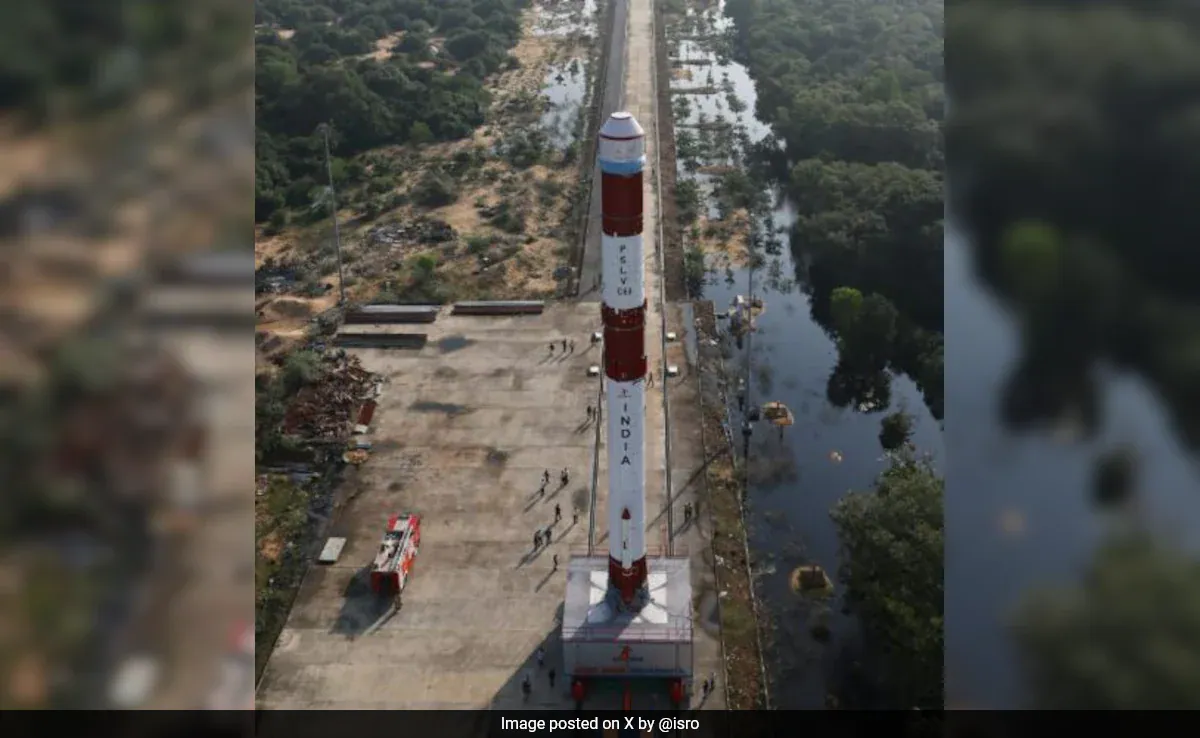
ISRO is set to conduct a variety of exciting experiments during the upcoming PSLV-C60 mission, which includes the fourth stage of its rocket known as the PSLV Orbital Experiment Module (POEM-4). This mission will focus on several innovative projects, such as demonstrating how seeds germinate in space, using a robotic arm to capture space debris, and testing eco-friendly propulsion systems.
The PSLV-C60 mission, scheduled for launch at the end of the year, aims to deploy two satellites named ‘Chaser’ and ‘Target.’ These satellites will be used to showcase space docking technologies that are essential for India’s future space station. POEM-4 will carry a total of 24 experiments, including 14 created by different ISRO labs and 10 from private universities and startups.

One of the key experiments involves growing cowpea seeds in a controlled environment. This project, called the Compact Research Module for Orbital Plant Studies (CROPS), will monitor the plants’ growth until they reach the two-leaf stage. Additionally, Amity University has created the Amity Plant Experimental Module in Space (APEMS) to study spinach growth in microgravity conditions. Both experiments will take place at the same time—one in space and the other on Earth.
Another exciting component of this mission is the Debris Capture Robotic Manipulator, designed by VSSC. This robotic arm will demonstrate its ability to capture tethered debris using advanced techniques like visual servoing and motion prediction.
Moreover, a startup named Manastu Space will test its Vyom-2U green propulsion system during this mission. This thruster uses a mixture of hydrogen peroxide and special additives as fuel, offering a safer alternative to traditional hydrazine.
Lastly, the Varuna payload from Piersight Space in Ahmedabad will showcase a Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) in a CubeSat format. This marks an important step towards creating a network of SAR satellites for continuous monitoring of maritime activities.
Overall, ISRO’s PSLV-C60 mission promises to be a significant advancement in various fields, from agriculture in space to innovative debris management and green propulsion technologies.